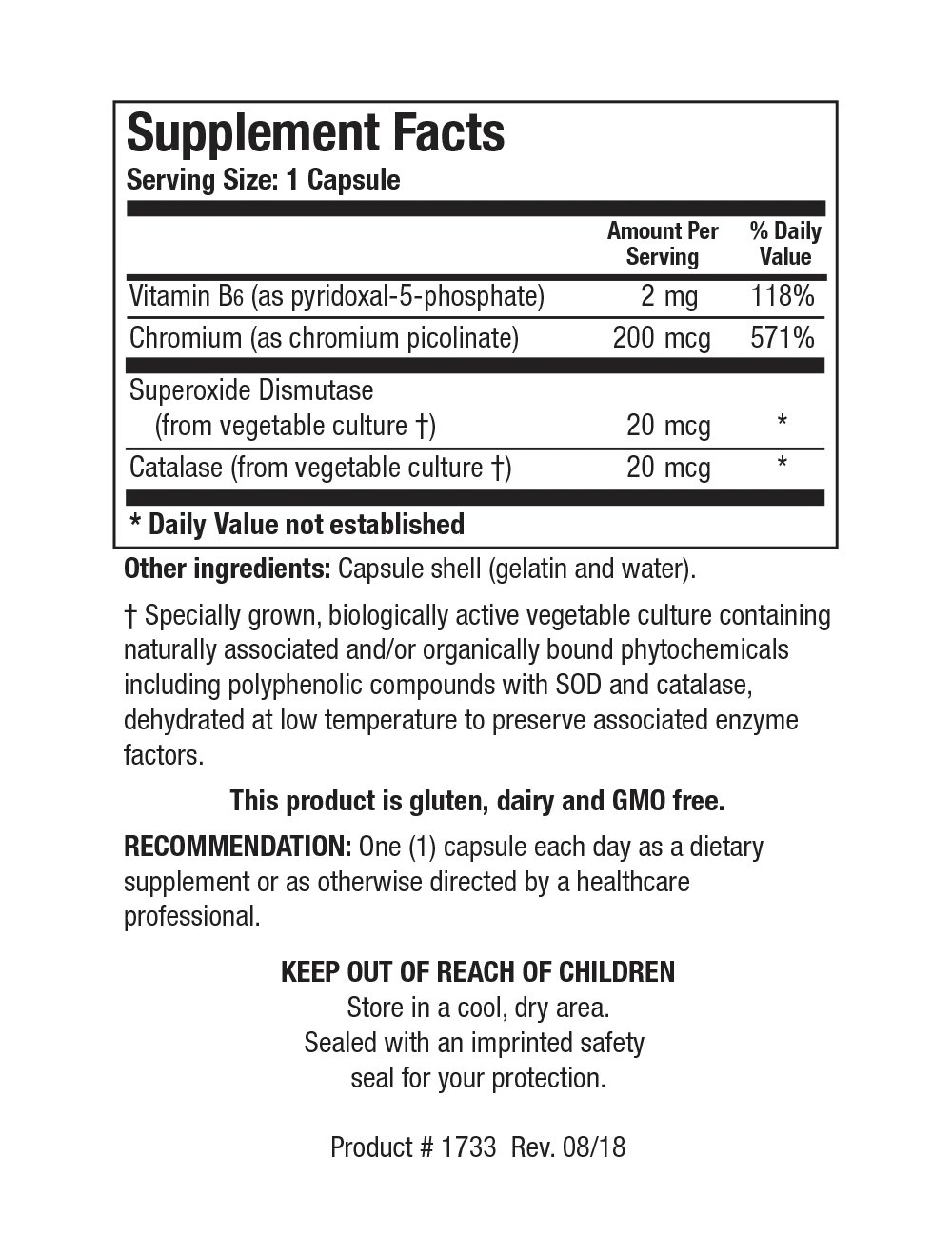
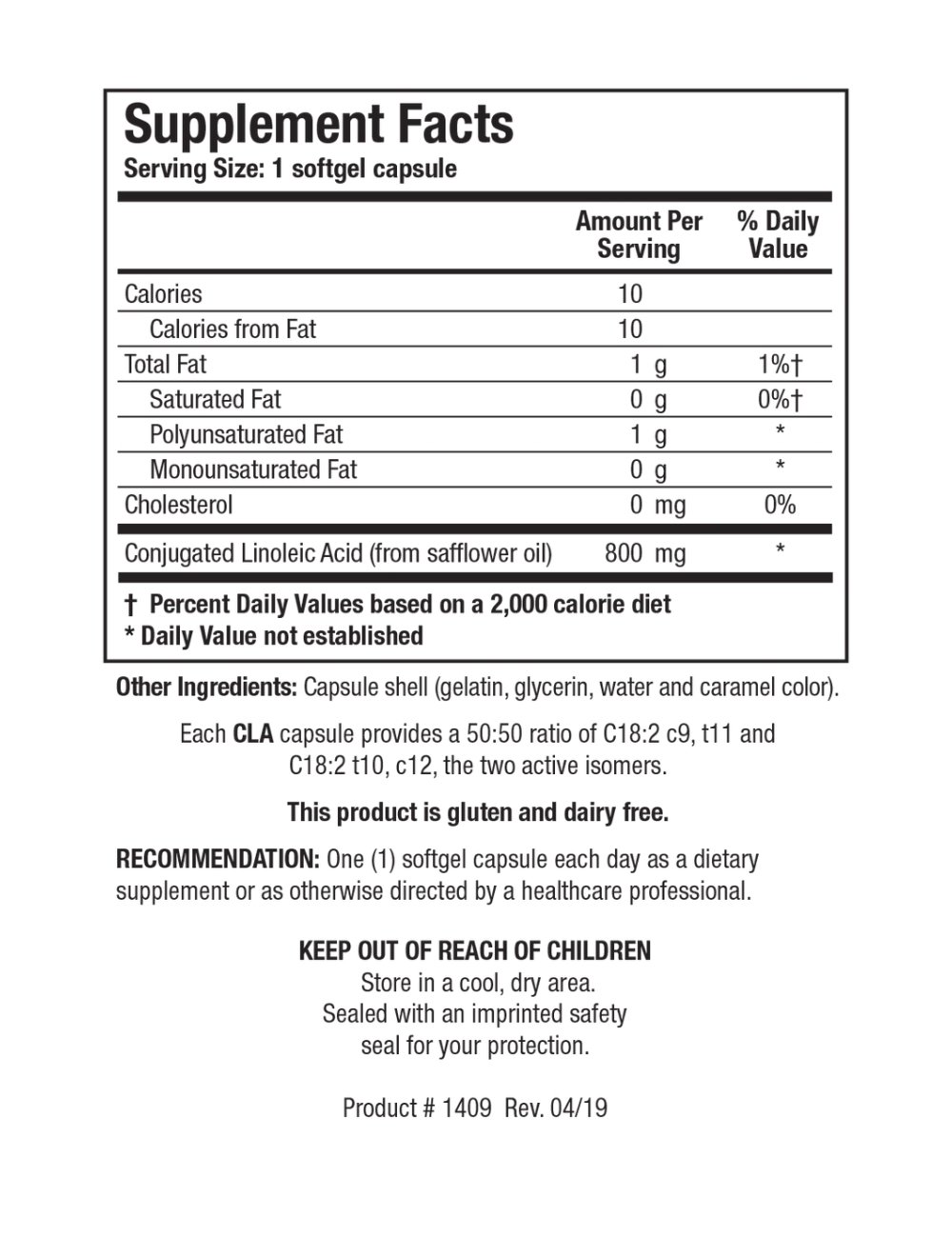
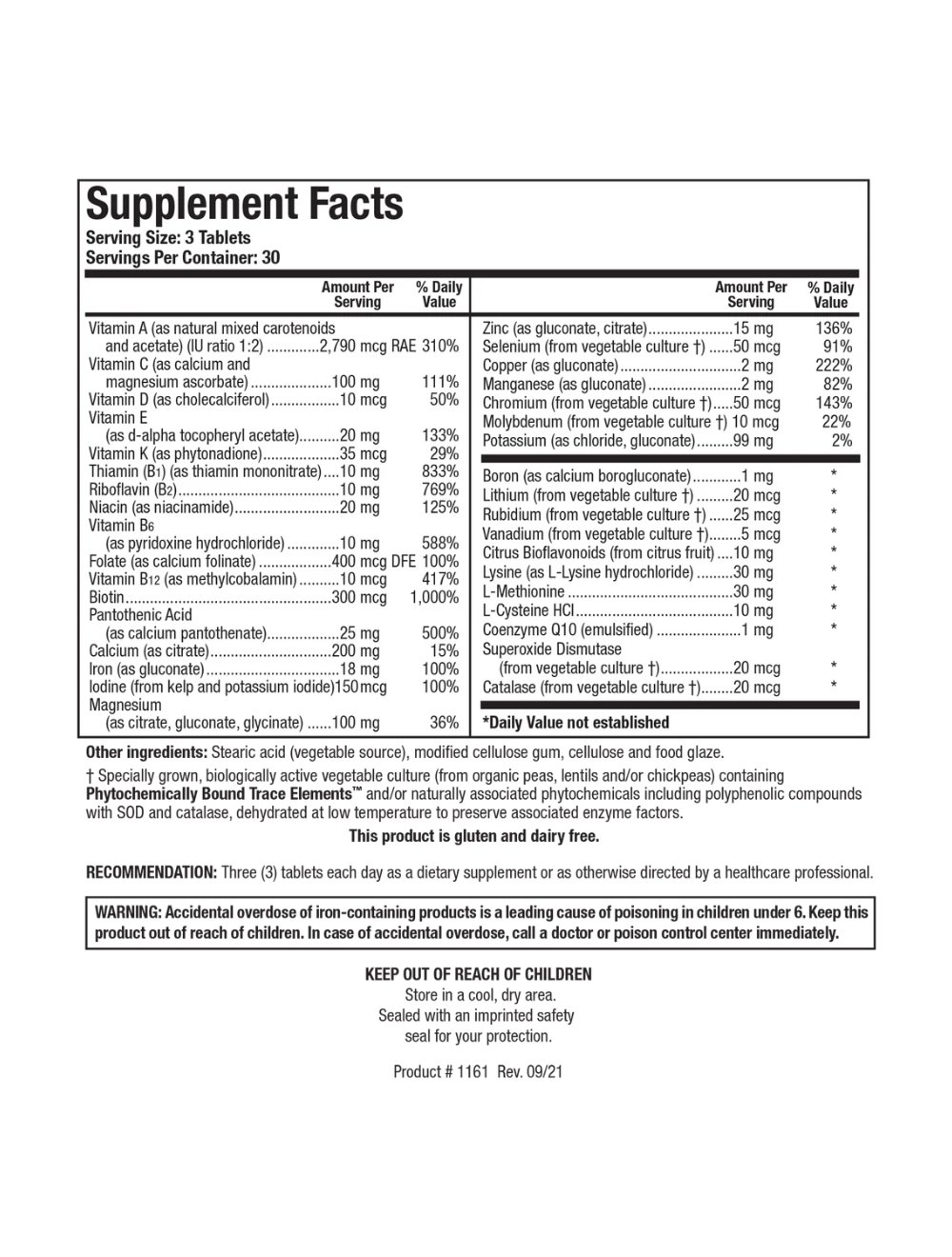
 Image 1 of 2
Image 1 of 2

 Image 2 of 2
Image 2 of 2



Gluterase®
Biotics Research Gluterase® has been designed to provide digestive support for those with gluten intolerance or sensitivity.
Gluten represents approximately 50% to 80% of the protein found in wheat, barley and rye grains, and primarily due to its rich proline content, can be very difficult to digest. Gluten can be found in many different foods as an additive, making it very difficult to avoid entirely, even when trying to follow a gluten free diet. It is for those patients that Biotics Research formulated Gluterase®. Gluterase® provides specific nutrients shown to help digest and inactivate gluten, and at the same time support the health and efficacy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.*
Biotics Research Gluterase® has been designed to provide digestive support for those with gluten intolerance or sensitivity.
Gluten represents approximately 50% to 80% of the protein found in wheat, barley and rye grains, and primarily due to its rich proline content, can be very difficult to digest. Gluten can be found in many different foods as an additive, making it very difficult to avoid entirely, even when trying to follow a gluten free diet. It is for those patients that Biotics Research formulated Gluterase®. Gluterase® provides specific nutrients shown to help digest and inactivate gluten, and at the same time support the health and efficacy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.*
Biotics Research Gluterase® has been designed to provide digestive support for those with gluten intolerance or sensitivity.
Gluten represents approximately 50% to 80% of the protein found in wheat, barley and rye grains, and primarily due to its rich proline content, can be very difficult to digest. Gluten can be found in many different foods as an additive, making it very difficult to avoid entirely, even when trying to follow a gluten free diet. It is for those patients that Biotics Research formulated Gluterase®. Gluterase® provides specific nutrients shown to help digest and inactivate gluten, and at the same time support the health and efficacy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.*